What did scientists discover?
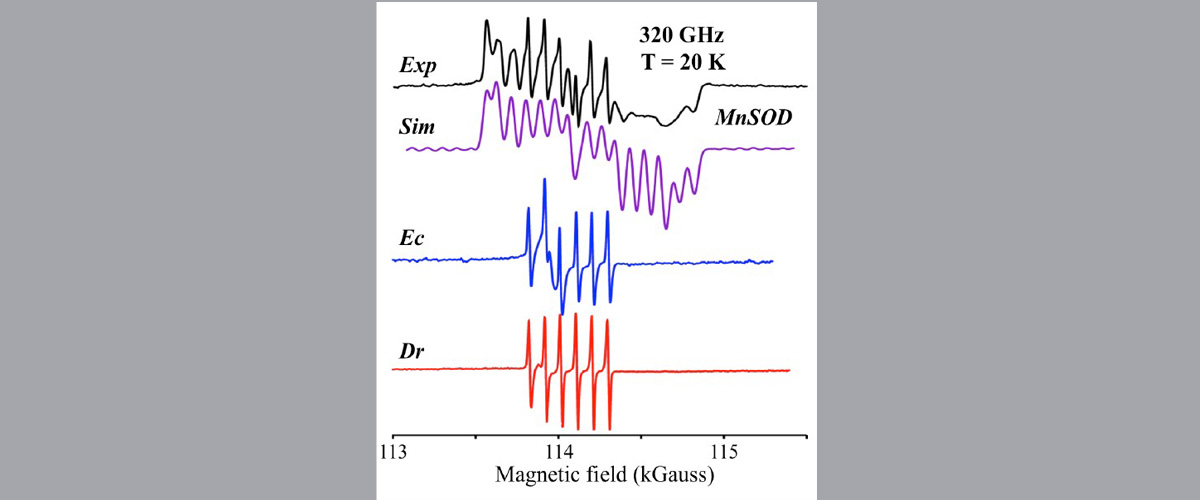
High field EPR Measurements performed on radiation resistant samples of Deinococcus Radiodurans (Dr) and Escherichia coli (Ec) show very little manganese superoxide dismutase (MnSOD) content.
Why is this important?
Evidence is mounting that small high-symmetry antioxidant complexes of manganous ions with metabolites (H-Mn2+) are responsible for cellular IR resistance, and that H-Mn2+ protects the proteome from IR-induced reactive oxygen species. This study disproves previous work suggesting that MnSOD is critical in the IR survival, and confirms that H-Mn2+ is the strongest known biological indicator of DNA repair efficiency and survival after gamma radiation exposure.
Who did the research?
A. Sharma1, E.K. Gaidamakova2,3, O. Grichenko2,3, V.Y. Matrosova2,3, V. Hoeke1, P. Klimenkova2,3, I. H. Conze2,4, R.P. Volpe2,3, R. Tkavc2,3, C. Gostinčar5, N. Gunde-Cimerman5, J. DiRuggiero6, I. Shuryak7, A. Ozarowski8, B.M. Hoffman1, M.J. Daly2
1Northwestern University; 2Uniformed Services University of Health Sciences; 3Henry M. Jackson Foundation for the Advancement of Military Medicine; 4University of Bielefeld; 5University of Ljubljana; 6Johns Hopkins University; 7Columbia University; 8National MagLab
Why did they need the MagLab?
High magnetic fields provide dramatically increased spectral resolution compared to much lower field commercial spectrometers. This facilitates discrimination of paramagnetic signals from biological samples that may potentially contain multiple species. In the present case, Dr exhibits a very sharp, six-line spectrum indicative of the highly symmetric H-Mn2+ species. In contrast, MnSOD exhibits a broad multiline spectrum indicative of a strongly anisotropic Mn2+ species.
Details for scientists
- View or download the expert-level Science Highlight, Across the Tree of Life: Radiation Resistance Gauged by High-Field EPR
- Read the full-length publication, Across the tree of life, radiation resistance is governed by antioxidant Mn2+, gauged by paramagnetic resonance, in Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci.
Funding
This research was funded by the following grants: G.S. Boebinger (NSF DMR-1157490); B. Hoffman (NIH GM111097); M. Daly (HDTRA1620354); I Shuryak (HDTRA1-15-1-0058); J. DiRuggiero (AFOSR FA9550-14-1-0118)
For more information, contact Stephen Hill.