What did scientists discover?
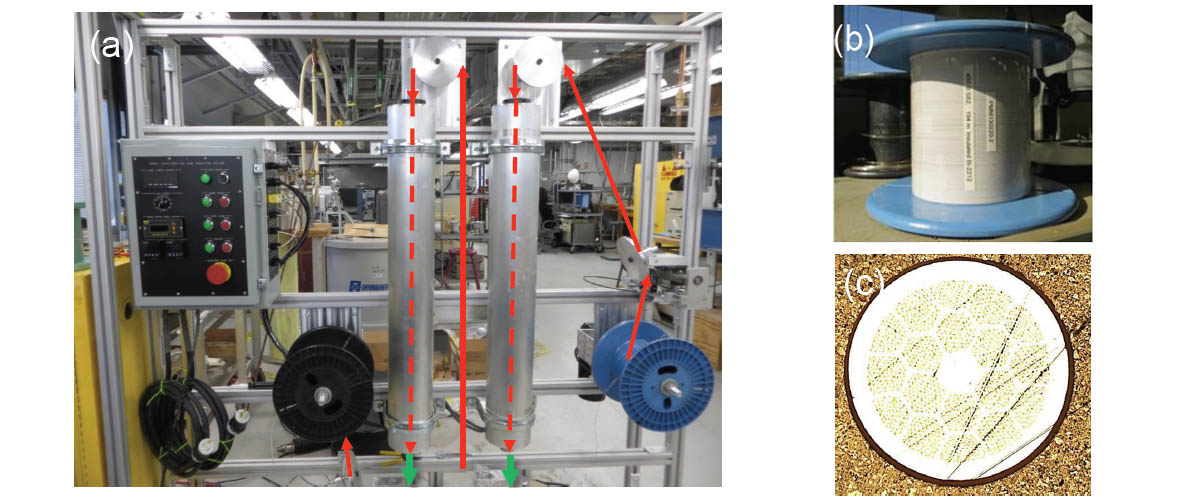
We have developed a titanium-oxide based ceramic coating for high-temperature superconducting round wire made from the superconductor Bi2Sr2CaCu2O8−x (Bi-2212). This novel coating has proven to be suitable for use as electrical insulation in superconducting magnets. The coating is applied to the wire using a continuous reel-to-reel dip-coating process. Arrows in Fig. a. (above) show the path of the wire from the blue spool-off reel, through the heaters (dashed lines) and twice into the dip vat (not shown, denoted by green arrows at bottom), and finally to the black spool-up reel.
Why is this important?
Bi-2212 is a superconducting wire that can be used to make a magnet that reaches magnetic fields well beyond any of today’s commercially-available magnets. Round wire is particularly valuable to achieve the highly uniform fields needed by chemists, biologists and doctors who use magnets for nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
The insulation is particularly challenging in this case, because it has to be flexible during magnet coil winding, yet able to withstand heat treatment of Bi-2212 (900 degrees Celsius), which would cause conventional polymer-based insulations to melt. This technology is the subject of a U.S. patent application.
Who did the research?
H.Kandel, J.Lu, J.Jiang, P.Chen, M.Matras, N.Craig, U.P.Trociewitz, E.E. Hellstrom and D.C. Larbalestier
National MagLab
Why did this research need the MagLab?
The MagLab is home to experts in both high-temperature superconductor development and magnet technology development. This insulation development required very close interactions and immediate feedback, only possible when the wire insulation development is carried out as a part of the Bi-2212 magnet technology development team.
Details for scientists
- View or download the expert-level Science Highlight, Ceramic Insulation for High-Temperature Superconducting Wire
- Read the full-length publication, Development of TiO2 electrical insulation coating on Ag-alloy sheathed Bi2Sr2CaCu2O8−x round-wire, in Supercond. Sci. Technol.
Funding
This research was funded by the following grants: G.S. Boebinger (NSF DMR-1157490)
For more information, contact Jun Lu.